4.3 Polynomials
Topics:
- polynomials
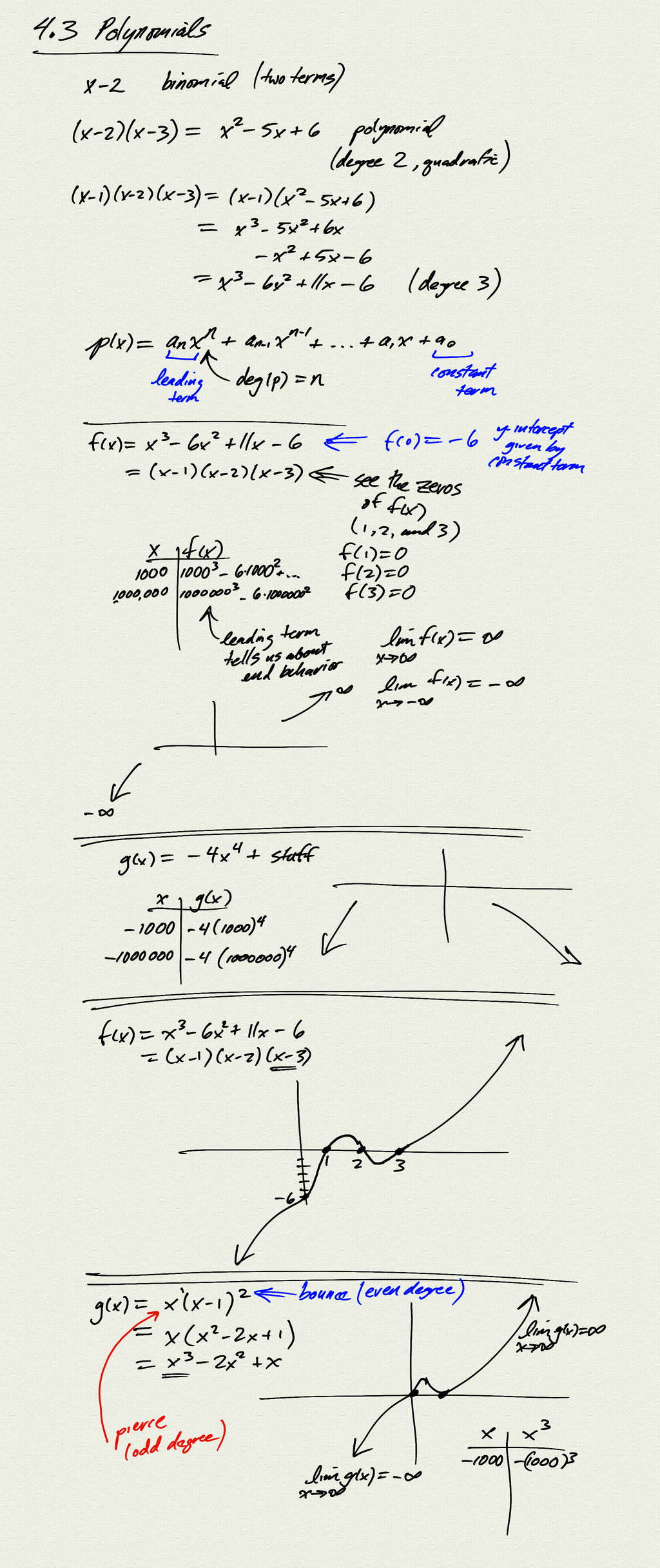
- $p(x) = a_n x^n + a_{n-1}x^{n-1} + … a_1 x + a_0$
- leading term $a_n x^n$, degree, and end behavior
- constant term $a_0$: y-intercept
- polynomial division
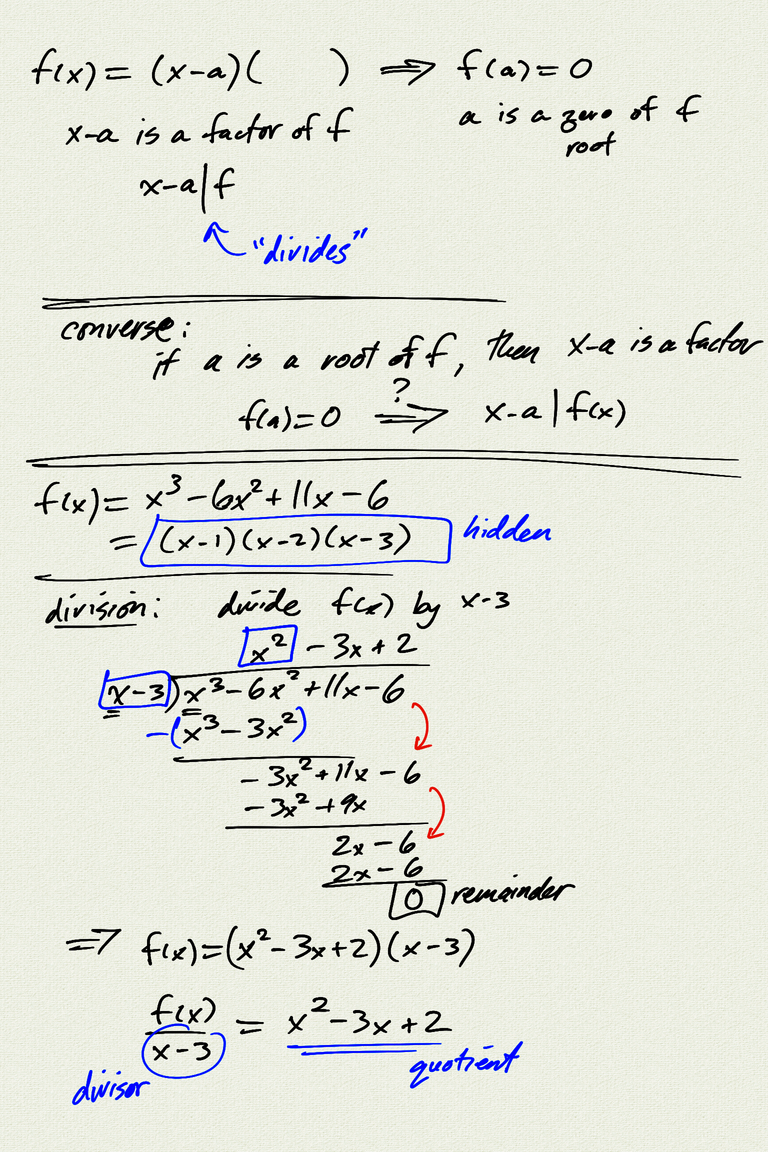
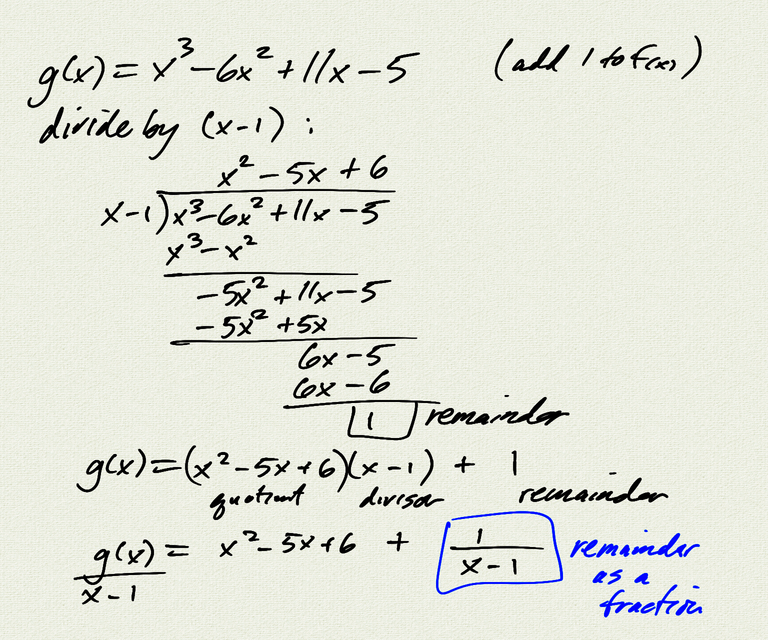
- dividing polynomial $p(x)$ by divisor $d(x)$ gives us a quotient $q(x)$ and
a remainder $r(x)$ with $\deg(r) < \deg(d)$
- $p(x) = q(x)d(x) + r(x)$
- $\dfrac{p(x)}{d(x)} = q(x) + \dfrac{r(x)}{d(x)}$
- dividing polynomial $p(x)$ by divisor $d(x)$ gives us a quotient $q(x)$ and
a remainder $r(x)$ with $\deg(r) < \deg(d)$
- Remainder theorem:
- $p(x) = q(x)(x-a) + r$
- When dividing a polynomial $p(x)$ by $x-a$, the remainder is $p(a)$.
- Factor theorem:
- $(x-a) \,|\, p(x) \quad\Leftrightarrow\quad p(a) = 0$
- $x-a$ is a factor of $p(x)$ $\;\Leftrightarrow\;$ $a$ is a root (zero) of $p(x)$
Reference:
OSP 3.4
OSP 3.5
OSP 3.6